Because of its climate and terrain, Algeria is heavily exposed to the risk of flooding by overflowing rivers, run-off and flash floods, potentially impacting on activities,
property and people.
 To assess potential risks associated with flooding, the Hydraulic Department of the Wilaya (DHW) Sidi Bel Abbes launched a pilot study for the delineation of flood areas using the hydrogeomorphological approach.
To assess potential risks associated with flooding, the Hydraulic Department of the Wilaya (DHW) Sidi Bel Abbes launched a pilot study for the delineation of flood areas using the hydrogeomorphological approach.
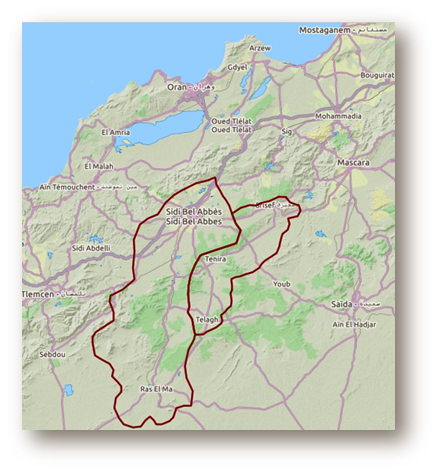
The methodology was applied to a 2500 km2 area covering the Oued Makerra and Oued Melghir catchments in the northwest of the country between Saïda and Tlemcen.
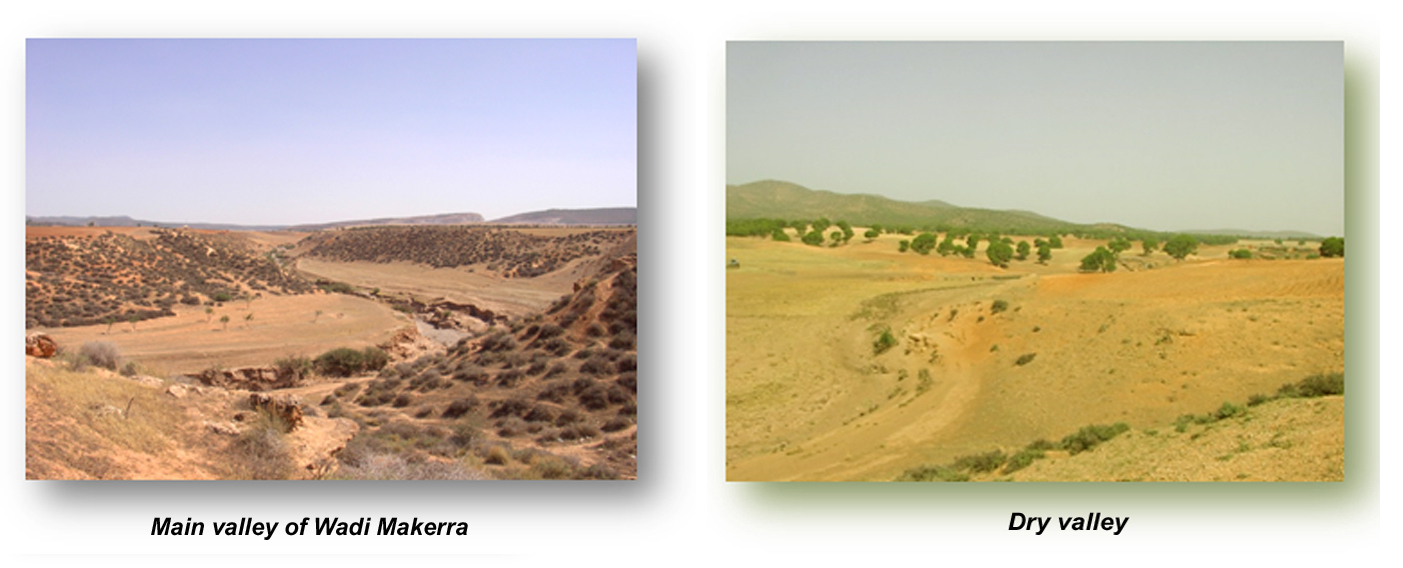
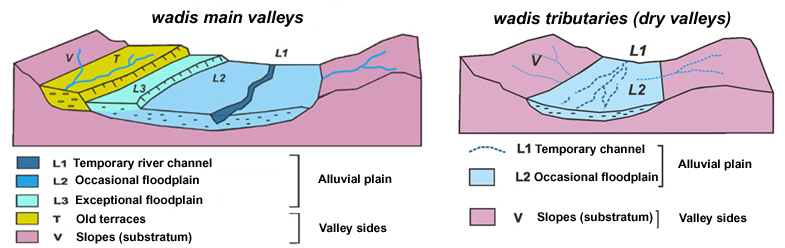
The method was adapted to account for the specific context of morphoclimatic arid and semi-arid wadis with temporary flows and dry valleys.
The flood risk map was produced in two stages:
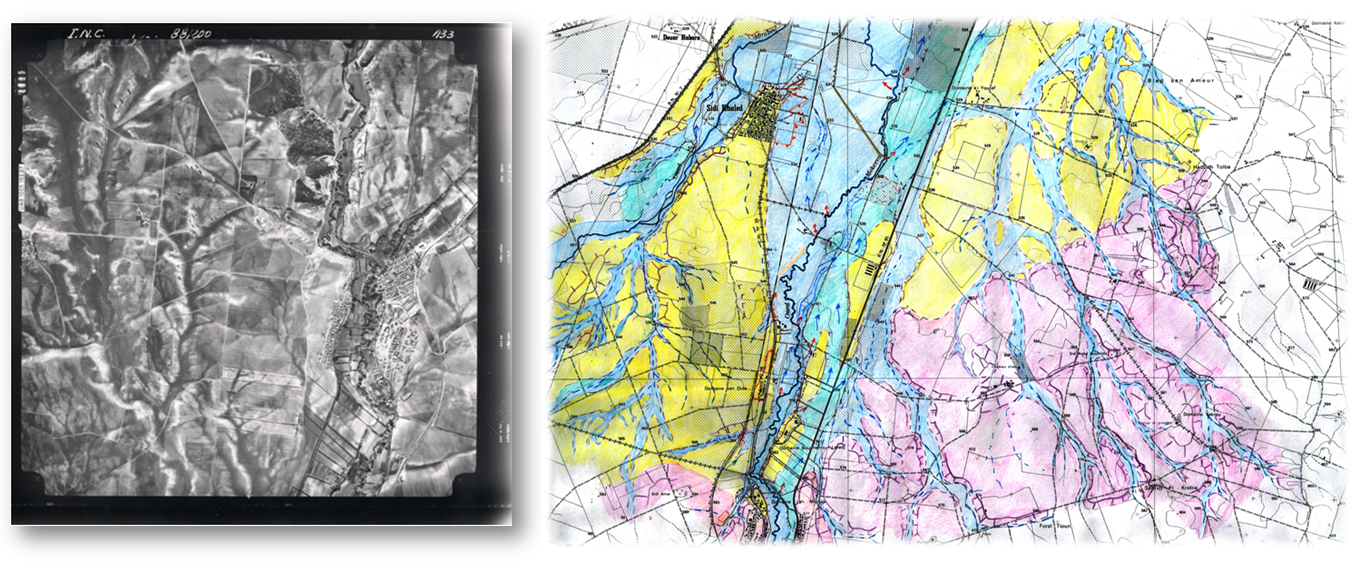
– Stage1 : interpretation of stereoscopic aerial photographs to map the morphology and the superficial drainage system.
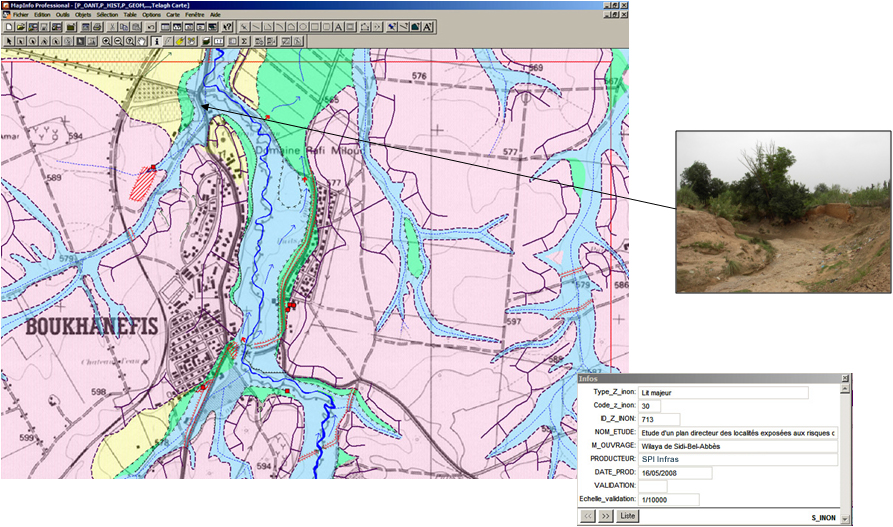
– Stage 2 : field assessment to refine the maps using indicators of hydrodynamic and geomorphological activity (erosion, sedimentology, solid transport), land use elements (waterproofing rate, impact of hydraulic structures ) and an analysis of past events (tracks, flood marks).
An atlas of 50 digital maps was produced and delivered in GIS format.
The maps have since been used by local government to develop a Water Management and Development strategy (2010) to control run-off and protect urban areas including the agglomeration of Sidi Bel Abbes through civil engineering works (e.g. dams, retention basins and flood relief channels).
This application illustrates the applicability of the hydrogeomorphological method to a wide range of climatic and morphological conditions.


You must be logged in to post a comment.